Talking Medicare: Prior Authorization Spending Update
Prior Authorization Data Shows Continued Reduction in Overall Spending on Dialysis Transports; Pendulum Swings Back Slightly in New Jersey and Pennsylvania
In May 2014, CMS announced the implementation of a three-year prior authorization demonstration project for repetitive scheduled non-emergency ambulance transports. This demonstration project was initially limited to the states of New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and South Carolina. These states were selected based on higher-than-average utilization rates and high rates of improper payment for these services. In particular, the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) had singled out these states as having higher-than-average utilization of dialysis transports in a June 2013 report to Congress.
Medicare payment data from calendar year 2015 showed the effect of the demonstration project. Total spending on dialysis transports was $559 million that year, down 22% from the year before. That correlates to a cost savings to the federal government of $158 million. Telling, $137 million (86%) of those savings came from the three states that participated in the demonstration project.
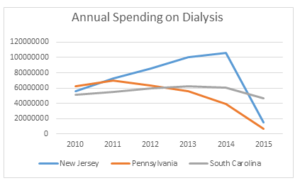
The chart to the right shows total spending on dialysis in those states in the years immediately preceding the implementation of the prior authorization project up through the first year of the project. While the three states had very different trajectories prior to 2015, each showed a significant decrease in payments under the demonstration project.
We now have Medicare payment data for 2016. This blog will focus on the second year of the prior authorization demonstration project. This includes tracking the effects of prior authorization on the five additional states (DE, MD, NC, VA, and WV) and the District of Columbia, which were added to the demonstration project for 2016.
Existing States
In the first year of the demonstration project, both New Jersey and Pennsylvania saw sizeable reductions (85.5% and 83.5%, respectively) in the total spending on dialysis transports. Both states saw dialysis payments rebound in 2016, with New Jersey increasing by 14.7% and Pennsylvania increasing by 3.7%. The financial community uses the phrase “dead cat bounce[1]” to describe a temporary recovery from a prolonged or pronounced decline. It is possible that explains why payments increased for these states in 2016. However, the more likely explanation is that Novitas, the Medicare Administrative Contractor in both states, recognized that the standards it used were overly restrictive during the first year of the project. If so, the increases in 2016 reflect the pendulum swinging back somewhat. If you accept that Novitas has reached an equilibrium point, total spending on dialysis in these states would be roughly 75% below pre-2015 levels.
By contrast, South Carolina saw total dialysis spending decrease by an additional 7.9% in 2016, over and above the roughly 25% reduction in 2015. Thus, spending in 2016 was roughly 30% lower than pre-2015 levels.
Expansion to New States
The follow charts track dialysis payments in the five states and the District of Columbia that were first subject to prior authorization in 2016. The chart on the left shows those states where the prior authorization project is administered by Novitas, while the chart on the right shows those states administered by Palmetto.
The phrase expresses the concept that even a dead cat will bounce if dropped from a tall enough height.
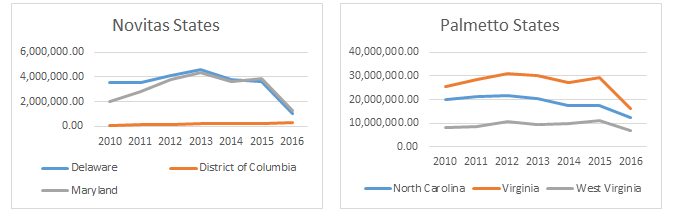
As you can see, both Delaware (72.3%) and Maryland (68.0%) showed sizeable reductions in total dialysis payments. Payments in the District of Columbia actually increased by 30%. However, a closer examination of the numbers shows that the increase was largely the result of an increase in the number of emergency transports to a hospital for dialysis, i.e., claims that fell outside the prior authorization project. Payment for scheduled BLS non-emergency transports fell 82.9% in the District, in line with reductions in the other two states.
The reductions in the Palmetto states was far more moderate, with reductions ranging from 27.8% (North Carolina) to 45.4% (Virginia). West Virginia saw a 36.0% decline.
Key Takeaways
With two years of experience under the prior authorization demonstration project, I think we can safely come to two conclusions:
- The implementation of a prior authorization process in a state will undoubtedly result in an overall decrease in the total payments for dialysis within that state; and
- The size of that reduction appears to be more dependent on the Medicare contractor than on any perceived level of over utilization.
The first conclusion should come as no surprise. Dialysis transports have long been the subject of scrutiny by the federal government. Moreover, the original states were not selected at random; they were selected based on data that suggested they were particularly suspect to over utilization.
The second conclusion is less intuitive. After all, Medicare coverage standards are intended to be national. While you could argue that a sizable reduction was expected for New Jersey and Pennsylvania, as there was evidence of widespread dialysis fraud in the Philadelphia metropolitan area, there was no basis to suspect widespread over utilization in Maryland or the District of Columbia. In fact, the District had only 58 BLS non-emergency dialysis transports in 2015, i.e., the equivalent of a single patient being transported for 2 months. Rather, the 2016 data suggests that Novitas has simply taken a far harder stance on dialysis than Palmetto.
This has potential implications beyond the demonstration project, which is scheduled to expire at the end of this year. As many of you know, the national expansion of prior authorization is part of the House of Representative’s ambulance relief bill (it is not mentioned in the corresponding Senate bill). The data suggests that the AAA must continue its efforts to work with CMS and its contractors on developing more uniform standards for coverage of this patient population.
Have an issue you would like to see discussed in a future Talking Medicare blog? Please write to me at bwerfel@aol.com.
[1] The phrase expresses the concept that even a dead cat will bounce if dropped from a tall enough height.